1. Introduction: Deconstructing AC Induction Motor Horsepower The AC Induction Motor is one of the m...
READ MOREIndustry News
2026-02-10
The quest for precise, reliable, and efficient motion control drives innovation across industries from medical devices to robotics and aerospace. At the heart of many advanced systems lies a sophisticated component: the worm gear brushless motors. This combination marries the irreplaceable mechanical advantages of a worm gear with the superior electronic performance of a brushless DC (BLDC) motor, creating a solution uniquely suited for demanding precision tasks. Understanding why this specific pairing excels requires delving into its inherent design benefits, from unparalleled positional holding to smooth, quiet operation under load. This article explores the distinct advantages of these integrated systems, illustrating why they are increasingly the preferred choice for engineers designing applications where accuracy, durability, and control are non-negotiable.
One of the most critical advantages of integrating a worm gear with a brushless motor is the inherent mechanical property of the worm gear set itself. In a standard worm gear configuration, the worm (the driving screw) can easily turn the gear, but the gear cannot turn the worm due to the high friction angle and the self-locking principle. This characteristic translates into exceptional backdriving resistance, meaning the output shaft holds its position firmly without requiring continuous power or an external brake. This is paramount in precision applications like robotic arms, surveillance camera gimbals, or adjustable medical tables, where maintaining a set position against external forces (like gravity or incidental loads) is crucial for safety and accuracy. The brushless motor component complements this by providing precise incremental movements when needed, but once the power is cut, the worm gear assembly locks the load securely in place. This synergy eliminates "drift" and enhances system safety.
To fully appreciate the holding power of worm gears, it's helpful to compare them with other common gearbox types used with brushless motors. While planetary and spur gears offer high efficiency and speed, their ability to prevent backdriving is minimal without additional components. This fundamental difference often dictates the choice of gearbox based on the application's primary need: dynamic motion vs. static holding. The following table contrasts key characteristics relevant to positional integrity.
| Gear Type | Backdriving Resistance | Typical Efficiency | Primary Advantage for Precision |
| Worm Gear | Very High (Self-Locking) | Moderate (40%-85%) | Excellent positional holding, compact right-angle drive |
| Planetary Gear | Low | High (85%-97%) | High torque density, low backlash, good for dynamic control |
| Spur Gear | Low | High (95%-98%) | Simplicity, cost-effectiveness for straightforward power transmission |
The geometry of a worm gear provides a remarkably high single-stage reduction ratio in a relatively small package. This allows a compact worm gear brushless motors to deliver very high output torque at low speeds – a characteristic often described as high torque density. This is precisely what many precision automation applications demand: slow, powerful, and controlled movements. Furthermore, the worm gear transmits power through a 90-degree angle. This right-angle configuration is a significant advantage of worm gear brushless motors for compact spaces, as it allows engineers to orient the motor parallel to the machine frame, saving valuable space and enabling more efficient and streamlined mechanical designs. This compact, high-torque package is ideal for applications like conveyor drives, automated packaging machinery, and small robotic joints where space is at a premium but performance cannot be compromised.
Precision applications, especially those in medical, laboratory, or consumer-facing environments, often mandate low acoustic noise and minimal vibration. The combination of a worm gear's sliding meshing action and a brushless motor's electronic commutation results in exceptionally smooth and quiet performance. Unlike the discrete steps of a brushed motor's commutator or the rolling impact of some gears, the worm gear's engagement is continuous and dampened. This makes worm gear brushless motors for quiet operation a top choice. Additionally, the absence of brushes in the motor eliminates a major source of electrical noise, arcing, and mechanical wear. This brushless design, coupled with the ruggedness of a well-lubricated worm gear set, leads to dramatically enhanced durability and longer service life with minimal maintenance, a key factor for brushless DC worm gear motor longevity.
The extended service life of a brushless DC worm gear motor is not accidental but the result of several synergistic design features. Understanding these factors helps in specifying the right motor for applications demanding high reliability and total cost of ownership. The primary wear components in traditional systems—brushes and gears with high rolling fatigue—are either eliminated or designed for durability. Proper selection and application can lead to tens of thousands of hours of maintenance-free operation. The table below outlines the key durability contributors and contrasts them with potential limitations.
| Durability Feature | Benefit | Consideration for Longevity |
| Brushless Motor Design | No brush/commutator wear; only bearing wear remains. | Requires quality bearings and proper thermal management for maximum life. |
| Worm Gear Material Pairing | Hardened steel worm with bronze alloy gear provides excellent wear resistance and shock absorption. | Proper lubrication is critical; dry running can cause rapid failure. |
| Encapsulated Gearbox | Protects gears from contaminants like dust and moisture, retaining lubrication. | Seal integrity over time and temperature cycles is important. |
| Efficient Thermal Design | Lower operating temperatures slow lubricant breakdown and preserve magnet & winding life. | Must be sized correctly for the duty cycle to prevent overheating. |
While the worm gear provides mechanical advantages, the brushless motor brings sophisticated controllability to the system. Modern brushless motors, driven by advanced 3-phase controllers, offer exceptional precision in speed regulation. This is a key aspect of speed control in worm gear brushless DC motors. The controller can modulate the current to the motor windings with great accuracy, allowing for very fine control over motor torque and rotational speed. When this is combined with a high-resolution encoder for feedback, the system achieves remarkable positional accuracy and repeatability. This precise control is essential for applications such as CNC tool changers, automated laboratory pipetting systems, and precision dispensing machines, where consistent, repeatable movements directly impact product quality and process reliability.
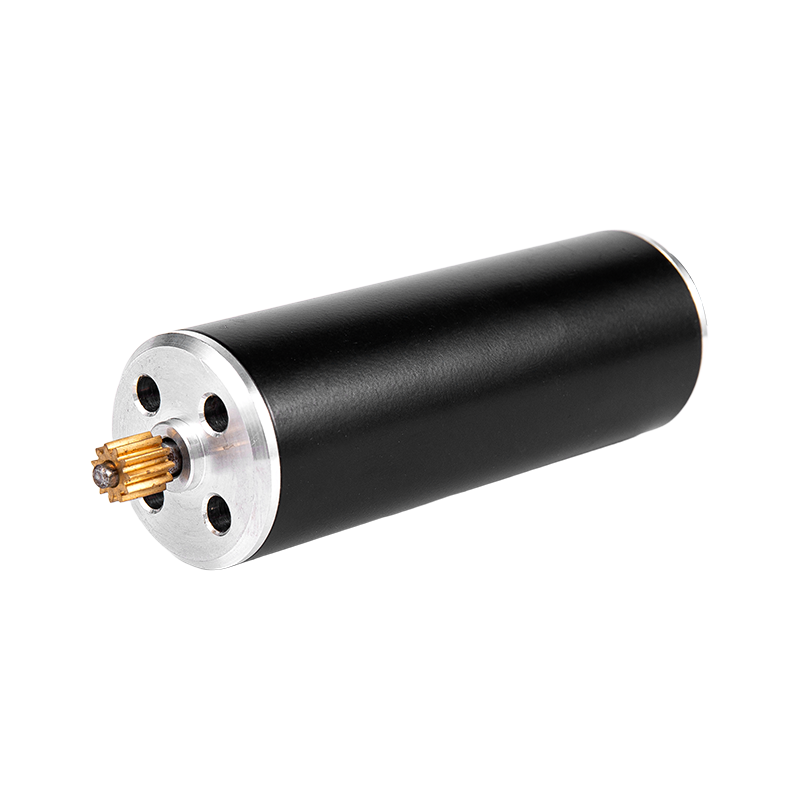

A common misconception is that worm gears are inherently inefficient. While their efficiency is lower than planetary gears in continuous high-speed operation, they excel in a specific, common regime: intermittent duty cycles and low-speed, high-torque operation. This aligns perfectly with the operational profile of many precision devices, which often move and then hold position. The brushless motor itself is highly efficient, converting most electrical input into mechanical power. In an intermittent duty cycle, the periods of zero holding current consumption (thanks to the self-locking gear) dramatically improve the *system's overall efficiency*. This makes them an efficient choice for intermittent duty applications like automated access panels, actuator-driven lids, or repositioning mechanisms that are active only a small percentage of the time. The overall system energy savings can be substantial.
The core difference lies in the gear mechanism and its resulting characteristics. A worm gear brushless motor uses a worm screw meshing with a gear wheel, providing high self-locking capability, a compact right-angle output, and high reduction in a single stage. It is ideal for applications requiring strong holding torque, positional integrity, and space-saving design. A planetary gear brushless motor uses a central sun gear, planet gears, and a ring gear, offering very high efficiency, low backlash, and excellent torque density in a coaxial (in-line) design. It is better suited for dynamic, continuous operation where efficiency and high-speed performance are critical, such as in CNC spindle drives or agile robotic arms. The choice depends on whether the priority is holding (worm) or dynamic motion (planetary).
Yes, they can be used for continuous operation, but careful selection and thermal management are crucial. While the worm gearbox has moderate efficiency, heat generation from friction is its primary limitation in continuous duty. For 24/7 use, specify a motor with a service factor rated for continuous duty, ensure the gearbox is properly lubricated for long life, and consider the ambient temperature. Applications involving very low output speeds or low torque loads are more forgiving. For high-torque, continuous operation, it is often necessary to oversize the unit or incorporate active cooling to dissipate heat and ensure the brushless DC worm gear motor longevity is not compromised.
Precise speed control in worm gear brushless DC motors is achieved through an electronic speed controller (ESC) or a more advanced servo drive. These controllers use Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) to regulate the voltage and current supplied to the motor's three phases. For open-loop speed control, a simple ESC receiving an analog or PWM signal may suffice. For highly precise speed regulation, especially at very low RPMs or under varying loads, a closed-loop system is essential. This involves using a controller that receives real-time feedback from an encoder or Hall-effect sensors on the motor. The controller constantly compares the actual speed to the commanded speed and adjusts the output accordingly, ensuring consistent performance essential for precision applications.
Traditional worm gear motors can be noisy, but modern worm gear brushless motors for quiet operation are engineered to minimize sound. Key factors influencing noise include gear tooth profile (e.g., using a helical or hourglass worm for smoother engagement), precise manufacturing to minimize gear meshing backlash, high-quality lubricants, and the use of brushless motors (which eliminate brush noise). When properly designed and manufactured, these motors can operate at sound levels below 50 dB(A), making them suitable for quiet office equipment, medical devices, and residential automation. Specifying a motor with "low-noise" or "silent" design features and ensuring it is not overloaded are the best ways to guarantee quiet performance.
One of the significant advantages is their low maintenance requirement. The brushless motor component is essentially maintenance-free, with no brushes to replace. The primary maintenance focus is on the worm gearbox. This typically involves periodic lubrication over the motor's extremely long service life. Many units are factory-lubricated with a lifelong grease suitable for the rated operating temperature range, requiring no end-user maintenance. In harsh environments or very high-duty-cycle applications, the lubrication interval may be specified in the manual. Other than that, simply ensuring the motor is kept clean, dry, and within its specified electrical and thermal operating limits is sufficient to ensure optimal brushless DC worm gear motor longevity.
1. Introduction: Deconstructing AC Induction Motor Horsepower The AC Induction Motor is one of the m...
READ MORE1. Introduction In modern industrial automation, data center construction, consumer electronics upgr...
READ MOREStepper motors represent a cornerstone of modern motion control, offering precise positioning and re...
READ MOREThe industrial motor landscape is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by the relentless ...
READ MORE